By The Biography Clearinghouse As we come to the end of another calendar year, we reflect upon how much the world can change in just a few short months. Political turmoil, violence, and war threaten the lives of millions. Climate scientists tell us that 2023 was the hottest year on record. Devastating fires and floods ravaged cities, towns, and forests alike. These catastrophes may feel unique to our life experience, so it helps to remember that people before us have faced hardships too. Again, we turn to biographies to learn from the people among us and those who came before us. What lessons in leadership can we find? How do artists, faith leaders, scientists, activists, educators, and others work towards goals? Handle setbacks? Cope with prejudice? Persevere while facing devastation? Work collaboratively to create change? In this year-end blog entry, we share a few picture book biographies from 2022 and 2023 that were inspiring to us, as well as preview a 2024 biography. With best wishes for peace in the New Year, The Biography Clearinghouse Team
Winter Hiatus Announcement
Interrogating History, Perspective, and Nonfiction Writing with Steve Sheinkin’s "Impossible Escape"10/10/2023
By Mary Ann Cappiello & Xenia Hadjioannou on behalf of the Biography Clearinghouse  Recently, the Biography Clearinghouse interviewed author Steve Sheinkin about his latest nonfiction book, Impossible Escape: A True Story of Survival and Heroism in Nazi Europe. Action-packed and filled with dramatic tension and intricate historical details, Sheinkin shares the experiences of Rudi Vrba and Greta Sidonová, two Jewish teenagers during World War II. While the full video interview and transcript are available on our website, covering a range of questions regarding Sheinkin’s research and writing processes, we share an edited portion of it here on the CLA blog as an example of the complex decision-making that goes into writing narrative nonfiction for tween and teen readers. Interview Question As you were working on the book and revising it, how did you balance crafting a narrative that builds tension, which as you mentioned earlier, gets the reader hooked and builds the narrative towards that climactic moment, and the need for exposition, which is oftentimes in the case of this book exposition about very difficult topics? What were the moments where you knew that you had to interrupt the action, pause the action to provide that information for your readers? Steve Sheinkin’s Answer (edited for brevity): That’s doing narrative nonfiction for middle grade and YA, I think. That's my career essentially, trying to figure out how to do that…… I used to write textbooks. That's… you see how hesitant I was to confess that? But I used to write history textbooks where they don't have that problem. It's all just boring facts and figures and names and dates. And so I just don't want to ever do that. I'm still sorry and making amends for doing that. So I want it to be just story. And then I realize, wait a minute. I can’t be. I get jealous of people who write for adults because they could just say, “and then Pearl Harbor happened,” and then everyone knows what that means. I can't do that, and fair enough I shouldn't be able to, because it's unfair of me to assume that someone who's 12 or 14 has that background information, and they shouldn't have to, to pick up the book. I think that's part of what makes this, hopefully, makes one of my books valuable, is that they don't have to have background information…. I guess I hope it works that I start with just story…I am seeing all the best scenes where there's really well documented moments that have those elements of a scene that you want as a writer. .. You don't need to know them right away, but you do need to know them pretty early on, and that's why the first third of a book like this is always the hardest part. It’s kind of like a juggling act once the balls are going. It's okay. But getting them all in the air in the right order is the hard part. And so I'll write little bits of context. In this case the rise of Adolf Hitler, what the Nazis were doing. How anti-semitism was such, so central, to what the Nazis did, and and all of that… I end up writing way too much of that, and I always do, and then kind of pare it down until it starts to feel right, and I work with my editor on that kind of stuff more than any other part of the book. I don't like to write the whole thing and then send it to her. I specifically like to try to write that first third as a draft and send it to her because it's just never, never good at first. It always has that problem of being clunky, and either not starting fast enough or we're not getting to the context soon enough, and those are kind of at odds with each other. You can get it right with enough back and forth, and trial and error… It's kind of like making a movie. You film both. You film all the scenes. You don't have to decide right away what order you're gonna edit them together in, but you know they're all going to be there.
Punctuating Narrative with Exposition
Embracing Point of View in Nonfiction Writing
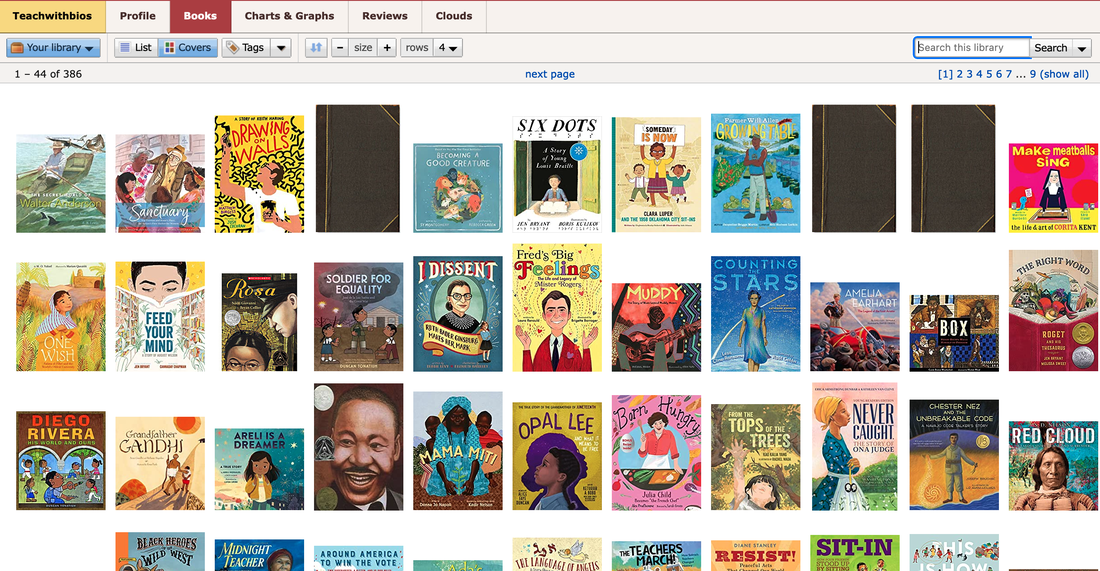
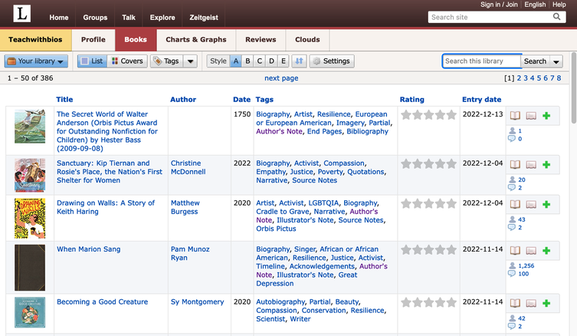
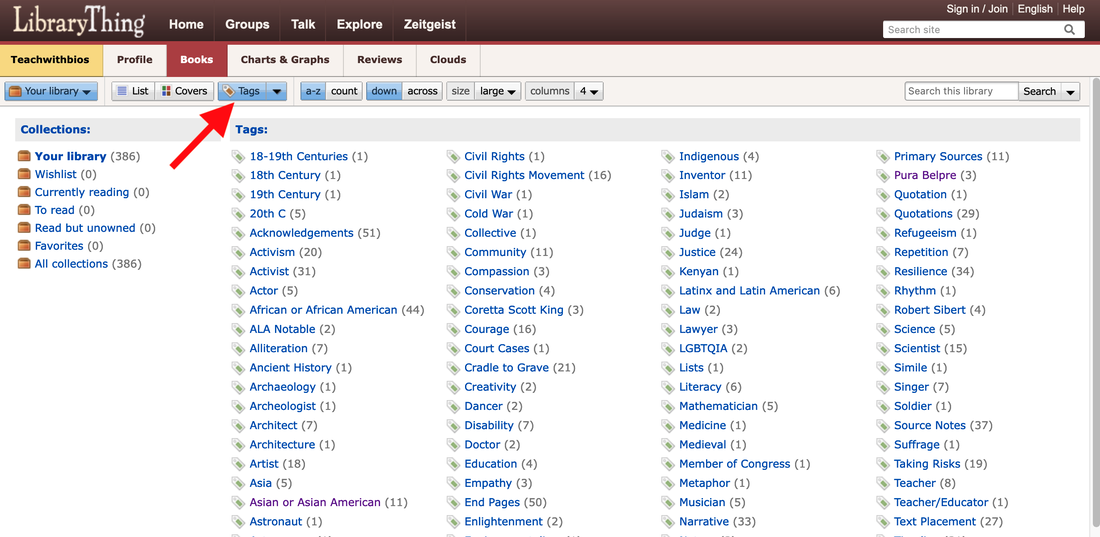
Mary Ann Cappiello teaches courses in children’s literature and literacy methods at Lesley University and is a founding member of The Biography Clearinghouse. She is co-chair of CLA's Expert Class committee and a former chair of NCTE’s Orbis Pictus Award for Outstanding Nonfiction K-8. Xenia Hadjioannou is associate professor of language and literacy education at the Berks campus of Penn State University. She is president of CLA and co-editor of the CLA Blog. She is a founding member of The Biography Clearinghouse. By Xenia Hadjioannou & Mary Ann Cappiello on behalf of the Biography Clearinghouse  Wondering how to find and curate biographies suited to the interests of your students or to your curricular needs? Frustrated by a piecemeal approach, cross-referencing booklists, award lists, and Google searches? The Biography Clearinghouse has a year end gift for you! We have created a collection of biographies for young people on LibraryThing, an online book cataloging service. The collection makes use of “tags” with which users can use to guide and focus their searches. This continually updated collection is intended as a tool for educators of all subjects and age groups, librarians, and anyone else who enjoys and works with biographies. We are busily tagging the books in our collection and will continue to add and tag more titles! The best part about it? You can access our collection for free and without having to sign up for an account. You can search the collection by theme, literary elements, geographic location, format feature, profession/discipline, etc. To learn how to access, navigate, and search through the Biography Clearinghouse Collection review the information below. How do I access the Biography Clearinghouse Collection?
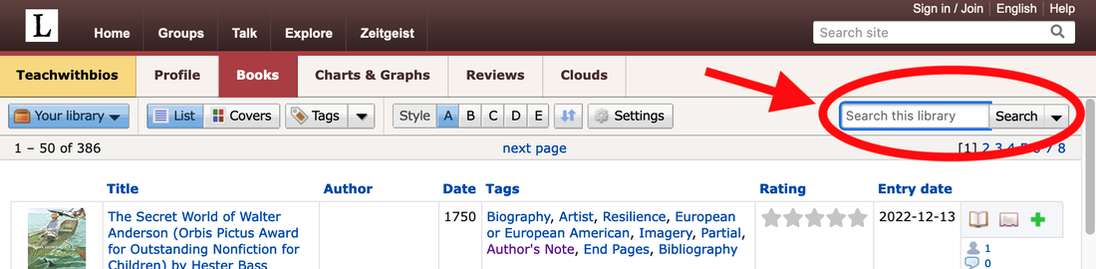
Simply go to https://www.librarything.com/catalog/Teachwithbios. There you will see our entire catalog listing. In the “Tags” column you will see all the tags assigned to each book by members of the Biography Clearinghouse.
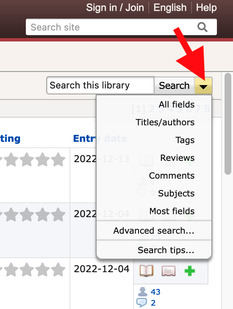
How do I search through your catalog?
Clicking on a tag will produce a listing of all books in our catalog we have annotated with it. Have any questions? Biographies to add to our collection? Suggested tags? Please email us at [email protected]. We’d love to hear from you. Xenia Hadjioannou is an Associate Professor of Language and Literacy Education at the Berks campus of Penn State University where she teaches and works with preservice teachers through various courses in language and literacy methodology. Xenia is the co-author of Translanguaging for Emergent Bilinguals. She is the Vice President and Website Manager of the Children's Literature Assembly, and a co-editor of The CLA Blog. Mary Ann Cappiello is a Professor of Language and Literacy at Lesley University, where she teaches courses in children’s literature and literacy methods. For twelve years, she blogged about teaching with children’s literature at The Classroom Bookshelf. She is a former chair of NCTE’s Orbis Pictus Award for Outstanding Nonfiction K-8. Mary Ann is the coauthor of Text Sets in Action: Pathways Through Content Area Literacy (2021). By Denise Dávila on Behalf of the Biography Clearinghouse
Using Viewfinders Sister Corita Kent authored provocative multimodal compositions that were inspired by looking closely at ordinary objects and were imbued with intertextual meanings. As suggested in Make Meatballs Sing, much of her work began by focusing her attention on specific elements and blocking out others. She employed cardboard viewfinders with her students as tools for developing the skill of looking. These next activities build upon the use of viewfinders in the classroom. They are adapted from the Make Meatballs Sing Curriculum Guide.
Denise Dávila is an assistant professor at the University of Texas at Austin. She studies children’s literature and researches the home literacy practices of families with young children in under-resourced communities. By Erika Thulin Dawes and Xenia Hadjioannou on behalf of the Biography Clearinghouse  We close out the school year immersed in social strife and conflict. Our students are grappling both with big questions about humanity and substantial uncertainties about everyday life. Recent research describes rising mental health concerns for young people (Acheson, 2020; Cowie & Myers, 2021; Samji et al. 2022) and it’s not surprising that maintaining optimism is challenging in the context of war, a global pandemic, and climate change. As educators, we are seeking ways to provide our students with grounding and with hope. And we believe that biographies, life stories of inspiring people, can help to provide both an anchor and inspiration. Our latest Biography Clearinghouse entry features Duncan Tonatiuh’s picturebook biography Soldier for Equality: José de la Luz Sáenz and the Great War. Using his trademark illustrative style, digital collage inspired by Mixtec Pre-Columbian art, Tonatiuh describes the World War I experiences of ‘Luz’; a teacher, activist, Texan, and a person with Mexican heritage. Toniatiuh’s biography of José de la Luz Sáenz is a powerful narrative of the transformative power of literacy. Luz’s education and multilingualism were instrumental in his life trajectory; his knowledge allowed him to navigate the battlefield safely, keeping him out of the trenches and instead in a fortified command post for the intelligence service. He developed his skills in organizing while teaching English to Mexican American soldiers. And upon his return to teaching when the war was over, he turned his outrage over unequal schooling for Mexican American children into activism, establishing the League of United Latin American Citizens (LULAC), an organization that helped to end the segregation of Latinx children from white schools. In our Biography Clearinghouse entry, we provide an interview with Duncan Tonatiuh and a collection of teaching ideas to support student exploration of Soldier for Equality. These teaching ideas encourage students to consider the transformative power of literacy and the generative power of community organizing and activism. They include: an exploration of translanguaging and theme development in picturebooks; a history of and contemporary look at the experience of minoritized populations in the United States army; a call to allyship to counter bullying; a visual literacy exercise exploring traditional artistic motifs; and a tribute to teacher activists. Below is an excerpt of the teaching ideas in the Biography Clearinghouse entry for Soldier for Equality: José de la Luz Sáenz and the Great War:
Teachers as Activists
Citations Acheson, R. (2020). Research digest: The impact of the covid-19 pandemic on child, adolescent, young adult, and family mental health. Journal of Child Psychotherapy, 46(3), 429-440. https://doi.org/10.1080/0075417X.2021.1912810 Cowie, H., & Myers, C. (2021). The impact of the COVID‐19 pandemic on the mental health and well‐being of children and young people. Children & Society, 35(1), 62-74. https://doi.org/10.1111/chso.12430 Samji, H., Wu, J., Ladak, A., Vossen, C., Stewart, E., Dove, N., Long, D., & Snell, G. (2022). Review: Mental health impacts of the COVID‐19 pandemic on children and youth – a systematic review. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 27(2), 173-189. https://doi.org/10.1111/camh.12501 Erika Thulin Dawes is a Professor of Language and Literacy at Lesley University where she teaches courses in children’s literature and early childhood literacy and is the program director of the graduate Early Childhood Education program. Erika is a former chair of NCTE’s Charlotte Huck Award for Outstanding Fiction for Children. Xenia Hadjioannou is an Associate Professor of Language and Literacy Education at the Harrisburg campus of Penn State University where she teaches and works with pre- and in-service teachers through various courses in language and literacy methodology. She is the Vice President and Website Manager of the Children's Literature Assembly, and a co-editor of The CLA Blog. The Bonnie Campbell Hill National Literacy Leader Award
|
|
Classified: The Secret Career of Mary Gold Ross, Cherokee Aerospace Engineer by Cherokee author Traci Sorell and Métis illustrator Natasha Donovan is an excellent example of a biography that features a woman in a STEM career. The book shows Mary’s love of mathematics and traces her path from teaching, to becoming Lockheed’s first female engineer, and then a member of the Skunk Works division working on satellites and spacecraft.
Extensive back matter includes a timeline, photos, an author’s note, an explanation of the Cherokee values mentioned in the text, source notes, and a bibliography. Illustrations showcase some of the aircraft Mary worked on such as the Lockheed A-12 and the Starfighter F-104C, as well as equations related to the projects. |
- Read the Smithsonian article “Mary Golda Ross: Aerospace Engineer, Educator, and Advocate.”
- Read the Smithsonian article “Mary Golda Ross: She Reached for the Stars.”
- Watch the Reading Rockets video: “Traci Sorell: Classified: Mary Golda Ross, Cherokee Aerospace Engineer.”
- Access the author’s website for additional materials that explore the Cherokee values Mary personified.
- There is also a Classified Teaching Guide which contains many activity ideas for experimenting with the forces of flight.
|
Blast Off! How Mary Sherman Morgan Fueled America into Space written by Suzanne Slade and illustrated by Sally Wern Comport is another of the untold stories of the space program. Working with two engineers as her assistants, Mary Sherman Morgan created the rocket fuel hydyne which powered the launch of the first American satellite into space. This biography explores Mary’s late start in school, her determination to pursue a career in chemistry, and her work at North American Aviation.
This book also has plenty of back matter with photos, a timeline, a selected bibliography, and more details about Mary, the Juno 1 rocket and the Explorer 1 satellite. The author’s note includes an explanation of how difficult it was to find information. She states, “Mary Morgan’s history is not well-documented. Unfortunately, that is true of many women who have made meaningful contributions to science and other fields.” Thanks to the author’s persistence in reaching out to family members, people from Mary’s hometown, and aerospace experts, she was able to create this inspiring story. |
- The book trailer shows the important launch Mary was working toward with her rocket fuel.
- This NASA video tells more about Explorer 1 and its lasting legacy for space exploration.
- NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory has a web page on Explorer 1 with links to photos, videos, and other information.
- In this short BBC video George Morgan talks about his mother and Rocket Girl, the book he wrote about her work developing rocket fuel.
- To make experiments of their own about the perfect fuel ratio for a rocket launch, students might enjoy working with fizzy rockets and trying out different proportions of water to Alka-Seltzer tablets to power the launch. SciTech Labs has posted a how-to video.
- There is also a lesson plan with instructions available from the Civil Air Patrol.
By Mary Ann Cappiello, Jennifer M. Graff and Melissa Quimby on behalf of The Biography Clearinghouse

Melissa Quimby, a 4th grade teacher in Massachusetts, has written the inaugural entry in our new feature “Stories from the Classroom.” Melissa is the genius behind #MeetSomeoneNewMonday, a weekly initiative that has spread from her classroom to her grade level team to an entirely different school in just three years.
This initiative launched when Melissa decided to share her passion for picturebook biographies with her students through interactive read-alouds. They were hooked! As Melissa writes, “Over time, I molded this project in intentional ways, and it evolved into an adventure that focused on identity, centered marginalized and minoritized communities, and cultivated thoughtful, strategic middle grade readers.” What started as a way to share nonfiction picturebooks as an engaging and compelling art form developed into a more nuanced exploration of global changemakers–past and present. With their weekly reading of picturebook biographies, students grow as readers and thinkers and deepen their individual and collective sense of agency.
In the following excerpts, Melissa describes how she reveals each week’s notable changemaker to her students and shares some of her picturebook biography selections.
Monday Read-Aloud Routines
 Reveal Slide Example
Reveal Slide Example Some weeks, interactive read aloud time happens on Monday morning immediately following the reveal. On some Mondays, it works best for us to huddle up in the afternoon. Occasionally, we steal pockets of time throughout our busy schedule to enjoy the biography of the week in smaller doses. When we read the text is not as important as how we read the text. The heart of this work truly lies in how we generate emotional investment within our students and how we help our students’ reactions and ideas blossom into new thinking about the world and ways that they can take action in their own lives for themselves and others. Sometimes, we simply read the biography to love it. In those moments, readers are silent with their eyes glued to the book, scanning the illustrations, wide-eyed when something surprising happens. Perhaps they whisper something to their neighbor, let out an audible gasp or share a comment aloud. Sometimes, we read to grow ideas. In these moments, readers are tracking trouble, considering how the figure responds to obstacles. They are ready to turn to their partner and reach for a precise trait word or theme and supporting evidence.
You can also reach out to Melissa through her website (QUIMBYnotRamona) or Twitter (@QUIMBYnotRamona) to discuss how to implement #MeetSomeoneNew initiative in your classroom or school.
Inspired by Melissa’s picturebook biography initiative or done something similar? Share your ideas and stories with us via email: [email protected]. Or, chime in on Twitter (@teachwithbios), Facebook, or Instagram with your own #teachwithbios ideas and picturebook biography recommendations.
Mary Ann Cappiello teaches courses in children’s literature and literacy methods at Lesley University, blogs about teaching with children’s literature at The Classroom Bookshelf. She is a former chair of NCTE’s Orbis Pictus Award for Outstanding Nonfiction K-8.
Jennifer M. Graff is an Associate Professor in the Department of Language and Literacy Education at the University of Georgia where her scholarship focuses on diverse children’s literature and early childhood literacy practices. She is a former committee member of NCTE’s Orbis Pictus Award for Outstanding Nonfiction K-8, and has served in multiple leadership roles throughout her 16+ year CLA membership.
By Julie Waugh and Erika Thulin Dawes on behalf of The Biography Clearinghouse.

In the Biography Clearinghouse entry for Building Zaha, you will find an interview, in which Victoria Tentler-Krylov describes how her own education as an architect influenced her writing of Zaha Hadid’s story. You’ll find teaching ideas that focus on character development, mentoring, and goal setting, as well as ideas that build content knowledge about the relationship between architecture and nature, the design processes of architecture, and women leaders in the field. Like us, you will be inspired by the lessons that author/ illustrator Victoria Tentler-Krylov learned from studying the life of Zaha Hadid: “Trust your own voice. Trust your own vision.”
Here is an excerpt of the teaching ideas in the Biography Clearinghouse entry for Building Zaha:
Exploring Zaha’s Designs

- A Tour of Zaha Hadid’s Most Iconic Buildings from Google Arts and Culture
- 30 Projects That Define Zaha Hadid’s Style from Rethinking the Future
- At her death, the BBC created this short video that looks back on Zaha’s work.
- For a slightly longer look at her life, watch Curious Muse’s Zaha Hadid in 7 Minutes.
- Google Arts and Culture also has a site Zaha Hadid; Groundbreaking Architect and Visionary.
- Zaha Hadid’s Architects continues the work of Zaha Hadid. When she died in 2016 her company had 36 projects underway.
Another recent children's book biography about Zaha Hadid is The World is Not a Rectangle by Jeanette Winter. Winter’s book focuses heavily on how Zaha Hadid’s work is influenced by the natural world, whereas Tentler-Krylov’s book focuses more on Zaha the person. The paired texts could provide a powerful invitation for students to compare and contrast the different ways in which authors made choices about how to share a person’s life in picture book format.
Breaking Boundaries: Female Architects
|
Throughout her career, Zaha Hadid encountered stumbling blocks. In the Biography Clearinghouse interview, Victoria Tentler-Krylov describes how her research into Zaha’s life revealed that Zaha wondered how those obstacles related to her identities as a woman and as a Muslim. Women continue to be underrepresented in the field of architecture. After reading Building Zaha, introduce your students to the work of Maya Lin, by reading Maya Lin: Artist-Architect of Light and Lines (written by Jeanne Walker Harvey, illustrated by Dow Phumiruk, Henry Holt, 2017). Compare and contrast the lives, experiences, and accomplishments of these two renowned female architects. Extend your study of women in architecture, by exploring the digital resources below. Connect with a female architect in your community who is willing to share her experiences in the field with your students.
|
Women of Steel and Stone ARCHUTE: The 25 Top Female Architects Changing the Architecture Industry Black Architects on their Challenges, Successes, and Hope for the Future CULTURED: 15 Architects on Being Black in Architecture Early Black Female Architects MADAME ARCHITECT: "That [Most] Exceptional One": Early Black Female Architects by Kate Reggev |
Designing for Form and Function: Thinking Like an Architect
Some people told Zaha Hadid that form was more important to her than function. She was criticized that her creative, uniquely designed spaces did not use space as well as they could, or did not use space as efficiently as possible. This was part of why, early in her career, people told Zaha that she would only be a “paper architect” - an architect that would only have designs on paper and not made into buildings.
If you have 1-2 hours… |
If you have 1-2 days… |
If you have 1-2 weeks… |
Invite students to look closely at your own classroom. What do you notice about how it is formed? How well does the way it is designed help you learn? How could you improve your classroom’s design to make it a better place to learn? Record some ideas and make some initial sketches. |
Zaha Hadid started many of her earlier architectural plans with paint and brush. After sharing ideas about how the classroom could be improved and redesigned, invite students to use different media to create initial plans for a newly designed classroom, much the same way that she did. You may wish to share some of Zaha’s initial architectural artwork to inspire them. |
Zaha Hadid was one of the first people to predict that computers would transform the architectural design process. It is possible that computers allowed her to create some of the unique shapes and structures that many thought were not possible. Collaborate with a local architect who can demonstrate their use of computer programs in their process of design. Visit with the architect in person or by Zoom so that students can see the architect's sketches and final plans. Ask questions about how the architect considers form and function in their design. Discuss how plans become blueprints that serve as guides for the construction of a building. Invite your students to revisit the initial classroom design plans they created with an eye for the relationship between form and function. How does the structure of the classroom they have created relate to its proposed use? Pair students so that they can describe their classroom plans to a classmate to get feedback. Next, ask students to create a more blueprint-like sketch of their envisioned classroom. Some students may be up for the challenge to use Google Sketch Up to create a structure from its creative beginnings to a model that you can walk through virtually. |
Additional Resources:The Guggenheim Museum in New York has a repository interesting resources for teachers, with lesson plans, entitled Form Follows Function. Sebastian, S., Shankar, R. & Al Qeisi, S. (2018). Design approach of Zaha Hadid from vocabularies and design techniques. Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research. 5 (6), 495-503. |
Julie Waugh teaches 8th grade ELA at Smith Junior High and serves as an Inquiry Coach for Mesa Public Schools. She delights in the company of children surrounded and inspired by books. A longtime member of NCTE, and an enthusiastic newer member of CLA, Julie is a former committee member of NCTE's Orbis Pictus Award for Outstanding Nonfiction for Children.
By Jennifer M. Graff, Jenn Sanders, and Courtney Shimek on behalf of The Biography Clearinghouse
| Picturebook biographies are some of the best ways to get to know global change-makers, understand the immense sacrifices made when pursuing one’s passion, and recognize injustices that typically accompany activist work. They enable us to connect with the people behind the discoveries. Thanks to Teresa Robeson and Rebecca Huang’s (2019) award winning picturebook, Queen of Physics: How Wu Chien Shiung Helped Unlock the Secrets of the Atom we can meet Wu Chien Shiung (aka “Madame Wu”), a renowned female nuclear and particle physicist who transformed our understandings of physics and became an unwavering mentor to and advocate for women in science. While Wu Chien Shiung was overlooked for the Nobel Prize in Physics three times, a sampling of Wu Chien Shiung’s accomplishments in the table below, showcases why she is referred to as the “Queen of Physics” and “The First Lady of Physics.” |
A Sampling of Wu Chien Shiung’s Accomplishments and Accolades
(Robeson, 2019)
| The first woman to
She also received
The Biography Clearinghouse’s latest entry includes interdisciplinary teaching ideas and resources that
This entry also features interviews with Robeson and Huang about their inspirations for this picturebook biography, connections to Wu Chien Shiung, and details about their research and composing processes, among other interesting topics. Below are three instructional ideas from this entry. |
Mentoring Via Peer Conferencing
Teach the mentor/tutor to pay attention to the writer’s ideas before worrying about spelling conventions.
“Respect the writer and the writer’s paper.”
Make the writer feel comfortable, be an active listener, and don’t write on the person’s paper.
“Involve the writer by asking questions.”
Teach mentors/tutors to ask open ended questions that get the writer talking about their ideas, their writing purpose, or their process.
“Teach the writer.”
Mentors/tutors share writing strategies that can be applied to the current piece but also across other pieces, rather than just trying to fix or revise the one piece they are discussing.
“Encourage the writer.”
Mentors/tutors provide encouragement by noting something specific that the writer did really well and offering one or two suggestions for revision (p.127).
Teachers can also invite students to consider the role of mentorship in their own lives. Students can identify individuals who have served as mentors to them and explore mentorship patterns and practices that are helpful and empowering to them as learners.
Advocacy and Activism
- Yuri Kochiyama was a political activist from California who fought with Malcom X to work for racial justice, civil and human rights, and anti-war movements. She went on to work in the redress and reparations movements for Japanese Americans and continued to fight for political prisoners until she passed away in 2014.
- Pranjal Jain is an Indian-American activist who has been organizing since she was 12 years old. As a current undergraduate at Cornell University, she is the founder of Global Girlhood, a women-led organization that inspires intercultural and intergenerational dialogue in online and offline spaces.
- Stephanie Hu is a Chinese American who founded Dear Asian Youth while she was a high school student as a support website for marginalized young people as a result of the rise in anti-Asian racism and violence during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Anna May Wong was the first Chinese American movie star to appear in U.S. box offices. Although she was often relegated to smaller roles that perpetuated Asian stereotypes, her career spanned silent films, talkies, theater, and television, and she helped blaze the trail for Asian American performers after her. See Paula Yoo and Lin Yang’s (2009) picturebook biography, Shining Star: The Anna May Wong Story, published by Lee & Low Books.
Printmaking a Character for Fiction Writing
By using basic supplies such as styrofoam plates and markers for printmaking, students can create a character to print and use in their own creative story. Watch this short video of a teacher demonstrating the styrofoam printmaking process.
If you have 1-2 hours…. |
If you have 1-2 days… |
If you have 1-2 weeks… |
Each student can design a main character for a story they write, and then draw and marker-print the character on paper. In this activity, students will experience a process of printmaking that helps them understand the steps and all the work that goes into making printed images. |
After students create their printed character (see the If you have 1 to 2 hours . . . column), students can draft the story in which their character experiences a problem, challenge, or adventure. Based on their story, they can add a background setting in their picture to place their character in the context of their story. Students will simply draw the background setting and objects around their character on their printed picture. |
Students can print their character four to six times, on separate pieces of paper, to create a storyboard with multiple scenes. Save one of these prints to make a title page for the story. For this activity, we recommend students leave the background of the styrofoam plate empty so they can draw in different backgrounds as the story progresses. Then, they can divide their corresponding written story into sections (three, four, or five, depending on the number of prints they made). For each story section, they can draw in a related background setting, additional characters, or objects to help complete the scene. In the end, they will have a multimedia print that has their character marker-printed and the background drawn in with pen, marker, or other tools. |
Reference
Jennifer Sanders is a Professor of Literacy Education at Oklahoma State University, specializing in representations of diversity in children’s and young adult literature and writing pedagogy. She is co-founder and co-chair of The Whippoorwill Book Award for Rural YA Literature and long-time member of CLA.
Courtney Shimek is an Assistant Professor in the department of Curriculum & Instruction/Literacy Studies at West Virginia University. She has been a CLA member since 2015.
by Xenia Hadjioannou, Lauren Liang, Liz Thackeray Nelson (Editors of the CLA Blog)
Published with permission | Transcript
Out of the Darkness Grows the Light
María also referenced a recently published children's biography of Corita Kent written by Matthew Burgess and illustrated by Kara Kramer: Make Meatballs Sing: The Life and Art of Corita Kent. The biography, which was composed in close collaboration with the Corita Center and includes reproductions of her work, was recently selected as one of the 2022 Orbis Pictus recommended books.
out of the darkness
|
Golden Line Strategy
|
Another children's title María Fránquiz connected to the 2022 NCTE Conference theme of ¡Sueños! Pursuing the Light is a picturebook by Yuyi Morales published as Bright Star in English and Lucero in Spanish. In this book, a young fawn explores a border territory, gently guided and encouraged by a maternal voice.
Using the golden line strategy, María pulled out the line: "No matter where you are, you are a bright star inside our hearts." "Dondequiera que estés, eres un lucero en nuestros corazones." In reflecting on the excerpt, María commented, "For me, this line embodies, the belief of light within each person, child or adult. It is repeated in different forms in the story. The message offers protection to children because it presents the possibility of a caring person or community somewhere. This line radiates hope and love. I think that line also ties nicely with the lighthouse logo that incorporates our theme for the 2022 Convention. With the moon, and the stars brightly shining and the constellation beyond the lighthouses of our different parts of the world." If you are interested in learning more about the golden line strategy, check out our post From the 2020 Notable Children’s Books in the Language Arts in which Jeanne Fain, the 2020 Notables Committee Chair, describes the strategy and offers ideas and recommendations for practice. Submitting Proposals for NCTE 2022
|
Lauren Aimonette Liang is Associate Professor at the Deparment of Educational Psychology of the University of Utah. She is Past President of CLA and co-editor of the CLA Blog.
Liz Thackeray Nelson is a doctoral candidate at the University of Utah. She is co-chair of CLA's membership committee and co-editor of the CLA Blog.
Authors:
CLA Members
Supporting PreK-12 and university teachers as they share children’s literature with their students in all classroom contexts.
The opinions and ideas posted in the individual entries are those of the individual authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions or views of CLA or the Blog Editors.
Blog Editors
contribute to the blog
If you are a current CLA member and you would like to contribute a post to the CLA Blog, please read the Instructions to Authors and email co-editor Liz Thackeray Nelson with your idea.
Archives
May 2024
April 2024
March 2024
February 2024
January 2024
December 2023
November 2023
October 2023
September 2023
August 2023
May 2023
April 2023
March 2023
December 2022
November 2022
October 2022
September 2022
August 2022
June 2022
May 2022
April 2022
March 2022
February 2022
January 2022
December 2021
November 2021
October 2021
September 2021
August 2021
June 2021
May 2021
April 2021
March 2021
February 2021
January 2021
December 2020
November 2020
October 2020
September 2020
August 2020
June 2020
May 2020
April 2020
March 2020
Categories
All
Activism
Advocacy
African American Literature
Agency
All Grades
American Indian
Antiracism
Art
Asian American
Authors
Award Books
Awards
Back To School
Barbara Kiefer
Biography
Black Culture
Black Freedom Movement
Bonnie Campbell Hill Award
Book Bans
Book Challenges
Book Discussion Guides
Censorship
Chapter Books
Children's Literature
Civil Rights Movement
CLA Auction
CLA Breakfast
CLA Expert Class
Classroom Ideas
Collaboration
Comprehension Strategies
Contemporary Realistic Fiction
COVID
Creativity
Creativity Sponsors
Critical Literacy
Crossover Literature
Cultural Relevance
Culture
Current Events
Digital Literacy
Disciplinary Literacy
Distance Learning
Diverse Books
Diversity
Early Chapter Books
Emergent Bilinguals
Endowment
Family Literacy
First Week Books
First Week Of School
Garden
Global Children’s And Adolescent Literature
Global Children’s And Adolescent Literature
Global Literature
Graduate
Graduate School
Graphic Novel
High School
Historical Fiction
Holocaust
Identity
Illustrators
Indigenous
Indigenous Stories
Innovators
Intercultural Understanding
Intermediate Grades
International Children's Literature
Journal Of Children's Literature
Language Arts
Language Learners
LCBTQ+ Books
Librarians
Literacy Leadership
#MeToo Movement
Middle Grade Literature
Middle Grades
Middle School
Mindfulness
Multiliteracies
Museum
Native Americans
Nature
NCBLA List
NCTE
NCTE 2023
Neurodiversity
Nonfiction Books
Notables
Nurturing Lifelong Readers
Outside
#OwnVoices
Picturebooks
Picture Books
Poetic Picturebooks
Poetry
Preschool
Primary Grades
Primary Sources
Professional Resources
Reading Engagement
Research
Science
Science Fiction
Self-selected Texts
Small Publishers And Imprints
Social Justice
Social Media
Social Studies
Sports Books
STEAM
STEM
Storytelling
Summer Camps
Summer Programs
Teacher
Teaching Reading
Teaching Resources
Teaching Writing
Text Sets
The Arts
Tradition
Translanguaging
Trauma
Tribute
Ukraine
Undergraduate
Using Technology
Verse Novels
Virtual Library
Vivian Yenika-Agbaw Student Conference Grant
Vocabulary
War
#WeNeedDiverseBooks
YA Lit
Young Adult Literature































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed