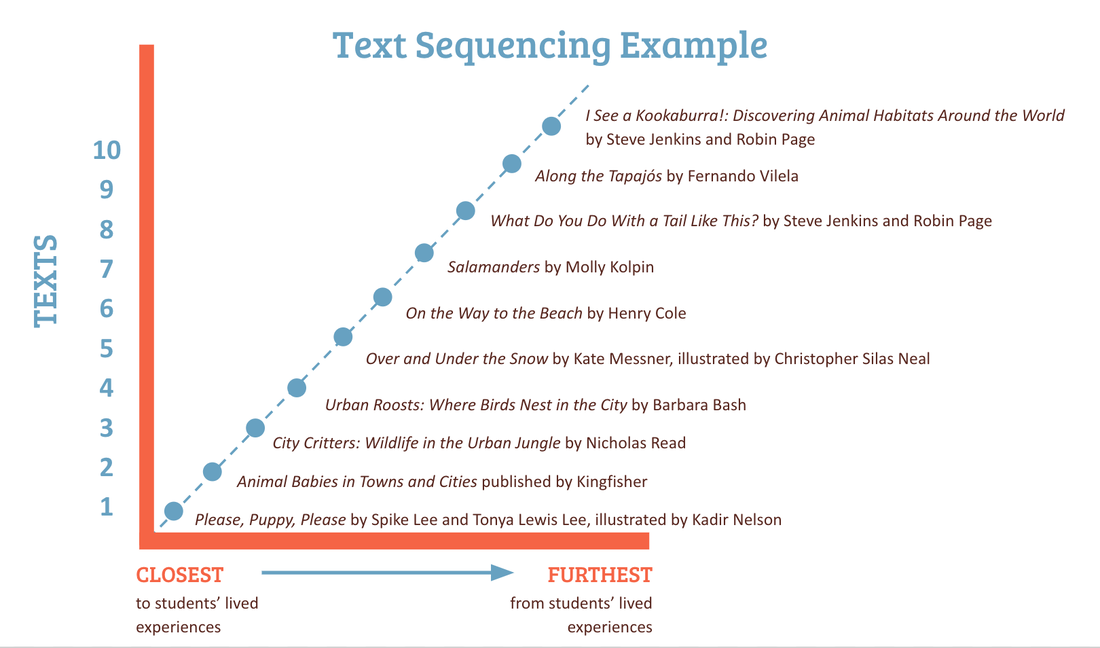
BY LIZ THACKERAY NELSON & MARGARET OSGOOD OPATZ 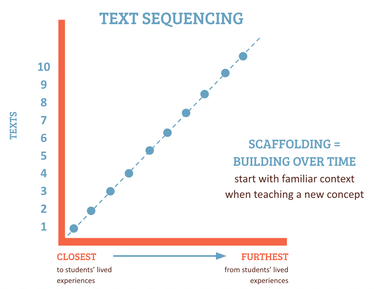 As former teachers, we are familiar with our students’ common refrain: “What does this book have to do with me?” Helping our students connect to what we teach in meaningful ways increases motivation, engagement, and overall learning (Guthrie & Wigfield, 2000). In this blog post we want to explore how creating and sequencing text sets to foster student background knowledge helps students make meaningful connections and increases reading engagement. The importance of readers’ background knowledge has been acknowledged for decades (Anderson, Reynolds, Schallert, & Goetz, 1977; Cunningham & Stanovich, 1998; Reynolds, Taylor, Steffensen, Shirley, & Anderson, 1982), yet in schools throughout our country readers are placed in texts that are decontextualized and reflect a lived experience very different from their own, making it challenging to construct meaning from the text and ultimately learn from it (Fleming, Catapano, Thompson, & Ruvalcaba Carrillo, 2015). This is particularly true when it comes to the informational content presented in science. To support readers in comprehending and learning from texts, teachers can reshape the curriculum by beginning with students’ lived experiences in mind. Reshaping the curriculum includes the use of high-quality literature sequenced in a way that begins with familiar content and contexts and then moves further from students’ lived experiences to the expected or mainstream curriculum. Learning about Animal Adaptations in an Urban Setting For example, when addressing science standards to teach about how animals adapt to their environment, many units of study focus on exotic animals such as those found in the Amazon Rainforest, the Serengeti, or Australian Outback--using texts such as I See a Kookaburra! (Jenkins & Page, 2005) , Biggest, Strongest, Fastest (Jenkins, 1997), or What Do You Do With a Tail Like This? (Jenkins & Page, 2008). While it certainly isn’t bad to teach about exotic animals and their unique ecosystems, to help students first understand how animals function in their unique habitat, it can be beneficial to begin with animals that are closer to students’ lived experiences. Therefore, before moving to texts that showcase exotic animals, we suggest using texts such as Please, Puppy, Please (Lee & Lee, 2005), Animal Babies in Towns and Cities (Kingfisher, 2005), City Critters: Wildlife in the Urban Jungle (Read, 2012), or Urban Roosts: Where Birds Nest in the City (Bash, 1992). These texts allow you to focus on animals that students who live in urban settings can observe in their own environment. Imagine students reading Urban Roosts: Where Birds Nest in the City (Bash, 1992), a book which illustrates several urban locations where birds live and nest (e.g., in a storefront light, under the awning of a building, on a statue that stands on a street corner, in a stoplight). Then, as students walk outside of their school building (or their homes if they are learning online right now), they start to notice the birds that roost on the building’s exterior doorways, creating firsthand experiences of animals adapting to their environments, and opportunities to talk about scientific content beyond the school texts and science class. When meeting as a class again, students discuss how the birds have adapted to and thrive in the urban environment. By situating school texts in familiar contexts, students are able to build background knowledge before being expected to grasp concepts in faraway, unfamiliar places. Because we live in an urban area, we would sequence our animal adaptation text set like this: Based on the area where you live, you may want to change the order of the texts. For example, salamanders are very common in some parts of the United States, so teachers in that area may want to move Salamanders by Molly Kolpin closer to the beginning of the text set. Explanation of Text SequenceCreating & Sequencing Your Own Text SetTo create and sequence text sets that begin with students' lived experiences and progress outward, we propose 5 steps:
ReferencesAnderson, R. C., Reynolds, R. E., Schallert, D. L., & Goetz, E. T. (1977). Frameworks for comprehending discourse. American Educational Research Journal, 14(4), 367-381. Cunningham, A. E., & Stanovich, K. E. (1998). What reading does for the mind. American Educator, 22, 8-17. Fleming, J., Catapano, S., Thompson, C. M., & Ruvalcaba Carrillo, S. (2015). More mirrors in the classroom: Using urban children’s literature to increase literacy. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield. Guthrie, J.T., & Wigfield, A. (2000). Engagement and motivation in reading. In M.L. Kamil, P.B. Mosenthal, P.D. Pearson, & R. Barr (Eds.), Handbook of reading research: Volume III (pp. 403-422). New York: Erlbaum. Reynolds, R.E., Taylor, M.A., Steffensen, M.S., Shirey, L.L., & Anderson, R.C. (1982). Cultural schemata and reading comprehension. Reading Research Quarterly, 353-366. Liz Thackeray Nelson is a doctoral student at the University of Utah in Educational Psychology. Her research interests include writing, multiliteracies, and children's literature. She is currently serving as the chair for the CLA Membership Committee. Margaret Osgood Opatz is a doctoral student at the University of Utah in Educational Psychology. Her studies include reading, literacy, and linguistics. She is a past recipient of the CLA Bonnie Campbell Hill National Literacy Leader Award. Comments are closed.
|
Authors:
|
CLA
About CLA
|
Journal of Children's Literature
Write for JCL
|
ResourcesCLA-sponsored NCTE Position Statements
|
Members-Only Content
CLA Video Library
|
© COPYRIGHT 2018.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed